EMBL-EBI’s Enzyme Motif Miner, Arc Institute's RESPLICE, and Harvard’s MEDEA
Kiin Bio's Weekly Insights
Welcome back to your weekly dose of AI news for Life Science!
What’s your biggest time sink in the drug discovery process?
🧬 Enzyme Motif Miner: Function Annotation Through Catalytic Geometry
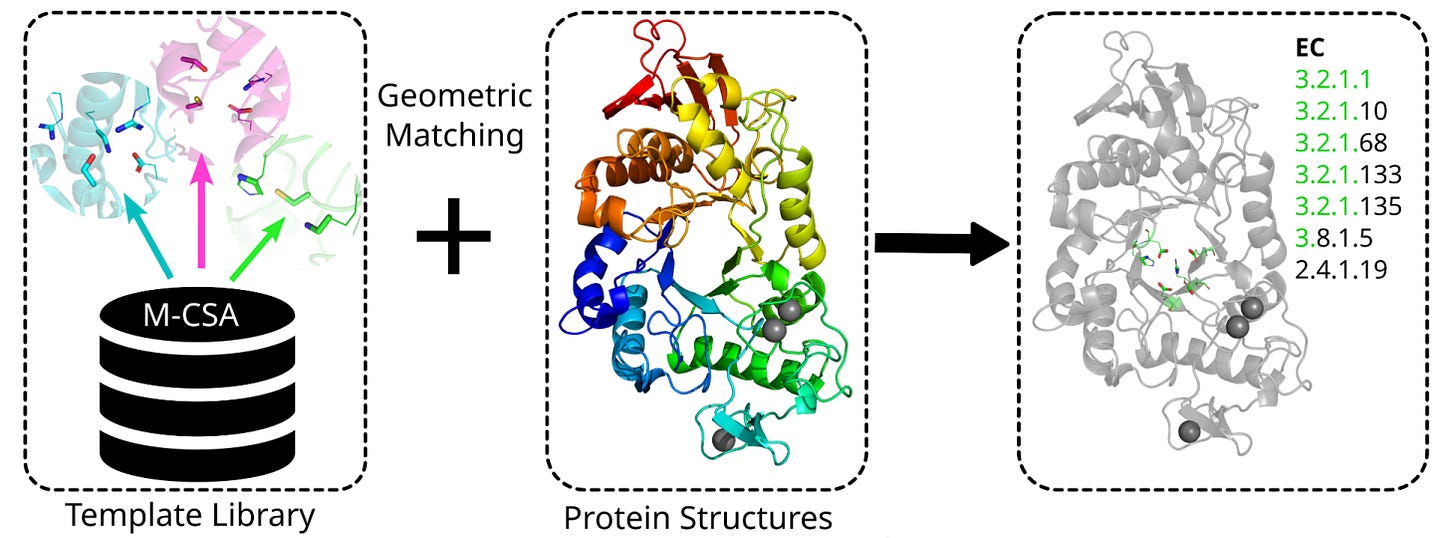
Identifying enzyme function by matching the geometry of catalytic sites
That is the core idea behind Enzyme Motif Miner, a tool from researchers at EMBL-EBI and Leiden University Medical Center. Rather than relying on sequence similarity, which breaks down below about 40% identity, it geometrically matches 3D arrangements of catalytic residues against a curated library of 6,780 templates from the Mechanism and Catalytic Site Atlas, M-CSA.
Every match traces back to experimentally characterised enzyme mechanisms, giving you biologically grounded annotations rather than black box predictions.
🔬 Applications and Insights
1️⃣ Outperforms sequence and structure alignment
Below 27.5% amino acid identity, sequence-based models perform no better than random. Enzyme Motif Miner stays predictive by leveraging conserved catalytic geometry, beating both amino acid and 3Di Foldseek alignment for distantly related enzymes.
2️⃣ Scales to the human proteome
Applied to 20,406 AlphaFold2-predicted human proteins, it matched 42% of annotated enzymes whilst hitting only 6.4% of non-enzymes. Of matched enzymes with UniProt active site annotations, 83.7% were correctly localised to the true catalytic site.
3️⃣ Uncovers convergent evolution
By combining low CATH fold similarity with high EC number agreement, the tool flags enzymes that independently converged on the same catalytic geometry, including metallopeptidases across seven distinct CATH superfamilies sharing antiparallel helix arrangements.
4️⃣ Fast enough for proteome-scale use
On a consumer laptop with 6 cores, it scans 1,000 human protein structures in under 4 minutes, 0.23 seconds per structure, two orders of magnitude quicker than AI-based tools like DeepFri.
💡 Why It’s Cool
Most function annotation tools are either fast but coarse, such as sequence alignment, or accurate but opaque, such as deep learning. Enzyme Motif Miner sits in a useful middle ground. It is knowledge driven, interpretable, and fast enough for AlphaFold-scale datasets.
The convergent evolution detection is particularly exciting. It suggests chemistry constrains biology in ways we can now systematically measure across entire proteomes.
📖 Read the paper
💻 Try the code
🧬 RESPLICE: Programmable RNA Rewriting Without Genome Editing
Rewriting RNA without touching the genome
That is the promise behind RESPLICE, a new tool from researchers at the Arc Institute, UC Berkeley, and Stanford University.
Most RNA editing tools can knock things down or swap single bases. But what if you need to replace an entire exon. That is where trans-splicing comes in, and it has been a frustratingly hard problem for decades.
RESPLICE changes that by combining two orthogonal CRISPR effectors, one to guide the trans-splicing reaction and one to block the competing cis-splicing reaction. The result is a programmable system that can write large RNA cargoes, up to 2.1 kb, into endogenous human transcripts with real efficiency.
🔬 Applications and Insights
1️⃣ High efficiency into endogenous transcripts
RESPLICE achieved up to 47% trans-splicing efficiency in unsorted cells across 11 endogenous human transcripts in 3 cell types, and up to 90% in cells sorted for high effector expression. Prior RNA-only approaches typically topped out around 5%.
2️⃣ A second CRISPR effector supercharges efficiency
Adding the cis-splicing interfering module, CIM, boosted trans-splicing by up to 28.8-fold for some targets, TFRC from 1.6% to 47.4%. It works orthogonally to the trans-splicing module, so combining the two is additive.
3️⃣ Therapeutically relevant targets demonstrated
Proof-of-concept correction in three disease contexts, hereditary haemochromatosis about 8%, C9orf72 repeat expansion linked to ALS and FTD about 10%, and TDP43 mutation replacement about 20%. These are precisely the genes where mutational heterogeneity makes site-specific editing impractical.
4️⃣ Off-target trans-splicing is low and stochastic
Transcriptome-wide RNA-seq showed on-target specificity averaging 95.3%. Off-target events occurred at less than 0.005% of all splice junctions, well below the basal splicing error rate of more than 0.1% per intron.
💡 Why It’s Cool
RNA medicine is having a moment, but most tools either edit single bases or deliver entire transgenes. RESPLICE fills an awkward gap. It enables large, programmable, transient edits at the transcript level without permanently altering the genome.
The transience is a feature, not a bug, particularly for diseases where reversibility or tunability matters.
📖 Read the paper
💻 Try the code
🧠 MEDEA: An Agent That Verifies Its Own Omics Reasoning
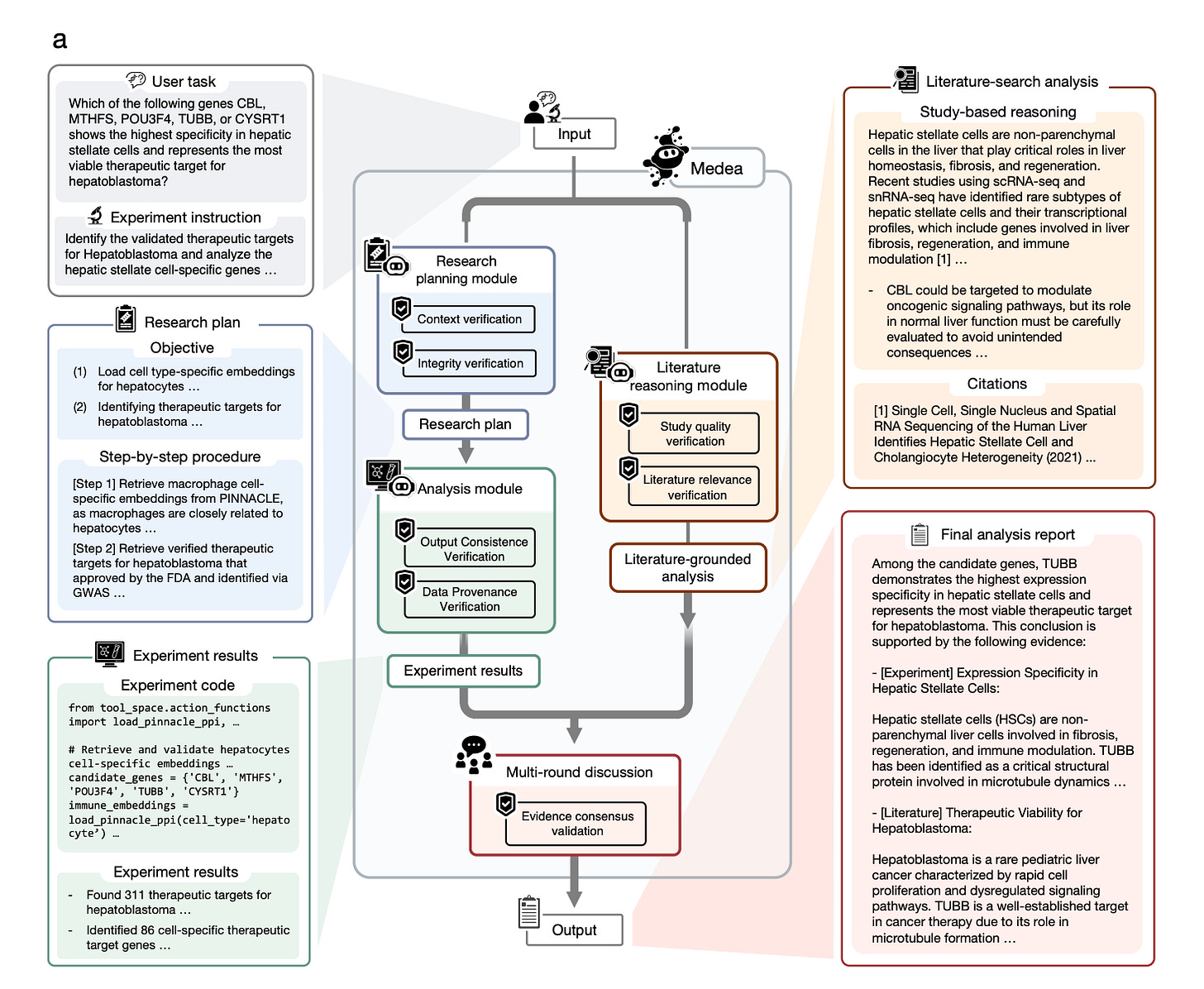
Turning an omics dataset into a therapeutic hypothesis is a long, messy process
That is precisely what MEDEA is designed to fix.
Built by researchers at Harvard Medical School, the Broad Institute, and Imperial College London, MEDEA is an AI agent that takes a biological objective and executes a transparent, multi-step omics analysis using 20 specialised tools, with verification built into every stage.
Most AI agents either hallucinate intermediate steps or follow rigid templates that break down across biological contexts. MEDEA is different. It verifies context, checks tool compatibility before and after execution, screens literature for relevance, and reconciles conflicting evidence before committing to a conclusion. When evidence is insufficient, it abstains rather than guesses.
🔬 Applications and Insights
1️⃣ Cell type specific target nomination
Across 2,400 analyses spanning five diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, Sjogren’s syndrome, hepatoblastoma, and follicular lymphoma, MEDEA outperforms standalone LLMs by up to 45.9%. It correctly resolves granular cell type distinctions that LLMs routinely collapse, such as naive versus effector memory CD4+ T cells in rheumatoid arthritis.
2️⃣ Synthetic lethality reasoning
Across 2,385 analyses in seven cancer cell lines, MEDEA improves accuracy by up to 21.7% over GPT-4o and correctly resolves over 323 cases where every tested LLM failed outright. It integrates DepMap co-dependency scores with pathway enrichment to flag gene pairs whose joint inhibition is predicted to kill cancer cells selectively.
3️⃣ Immunotherapy response prediction
Across 894 patient-level analyses from the IMvigor210 bladder cancer cohort, MEDEA achieves up to 23.9% higher accuracy than LLMs by integrating tumour transcriptomes, TMB, and microenvironment signatures. It rescues up to 50.9% of cases misclassified by the underlying ML model in the hardest subgroup, high TMB, non-inflamed tumours.
4️⃣ Verification beats volume
Ablations show a literature-only agent abstains 77.6% of the time, while an LLM-only agent abstains just 1.8% of the time but produces the most errors. The full MEDEA achieves the best accuracy with the lowest failure rate, demonstrating that structured verification beats simply adding more compute or retrieval.
💡 Why It’s Cool
MEDEA shows that the bottleneck in agentic biomedical AI is not raw reasoning power. It is the ability to stay grounded in biological context across long, multi-step analyses.
The calibrated abstention is particularly underrated. In drug discovery, a confident wrong answer is far more costly than an honest I do not know.
📖 Read the paper
💻 Try the code
Thanks for reading!
💬 Get involved
We’re always looking to grow our community. If you’d like to get involved, contribute ideas or share something you’re building, fill out this form or reach out to me directly.
Connect With Us
Have questions or suggestions? We'd love to hear from you!
📧 Email Us | 📲 Follow on LinkedIn | 🌐 Visit Our Website