EPFL’s GLDP, UO's CyclicMPNN, and UHN’s EchoJEPA
Kiin Bio's Weekly Insights
Welcome back to your weekly dose of AI news for Life Science!
What’s your biggest time sink in the drug discovery process?
🧪 GLDP: Latent-Space Protein Dynamics at All-Atom Resolution
🧪 Can we model protein motion without waiting hours for molecular dynamics?
That’s the goal of GLDP, a framework from researchers at EPFL and collaborators that simulates all-atom protein dynamics in latent space. Imagine teaching an AI to watch proteins move, then letting it choreograph new motions that still obey physics.
The problem with traditional MD is speed. Tracking every atom is accurate, but painfully slow, especially when rare events, like functional conformational changes, take forever to emerge. GLDP sidesteps this by simulating in a compressed representation, then decoding to full atomic detail.
🔬 Applications and Insights
1️⃣ Three propagators, one framework
They compared autoregressive neural networks, Koopman operators (linear dynamics), and score-guided Langevin methods. The neural net was the most stable for long rollouts. Langevin captured sharp side-chain detail. Koopman was lightweight, but a bit rigid.
2️⃣ Tested across scales
From alanine dipeptide to large GPCRs with 300+ residues. The autoregressive model managed 10,000-frame rollouts without collapse. Langevin recovered rotameric states with a Jensen-Shannon divergence of just 0.058.
3️⃣ Captured functional motions
On the A2A receptor, GLDP reproduced the activation pathway between inactive and active states — not just structure prediction, but full conformational switching tied to biological function.
4️⃣ Kinetic fidelity holds up
Using TICA analysis, they showed GLDP recovers physically meaningful timescales (650 steps for A1AR), where other models become unstable or lose temporal structure.
💡 Why It’s Cool
Most protein models generate snapshots. GLDP captures how proteins move, critical for drug discovery, where ligand binding often depends on timing and flexibility. By working in latent space, it’s also computationally lighter than brute-force MD, enabling rapid sampling of structural ensembles.
It’s honest about trade-offs too. Neural nets offer long-term stability. Score-based methods bring thermodynamic detail. No one-size-fits-all, and that transparency helps you choose the right tool based on your scientific goals.
📖 Read the paper
💻 Try the code
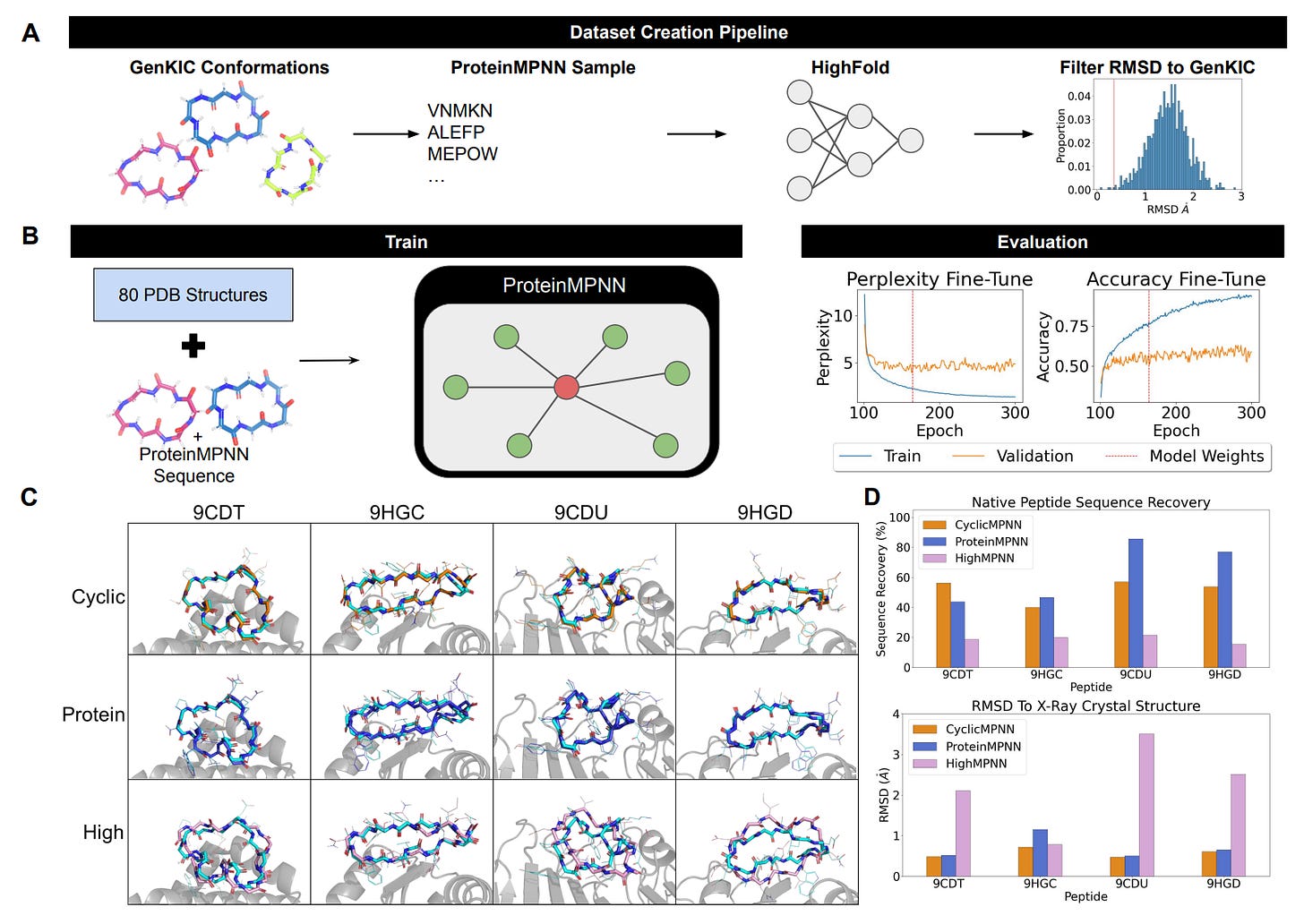
💊 CyclicMPNN: Teaching ProteinMPNN the Rules of Cyclic Peptides
Cyclic peptides are an important class of therapeutic molecules, acting as antibiotics, anticancer agents, and immunosuppressants. Compared to linear peptides, they show greater structural stability, resistance to proteolytic degradation, and improved binding specificity.
Although tools such as GenKIC and RFPeptide can generate realistic cyclic backbones, designing sequences that reliably fold into these constrained structures remains challenging.
🧬 ProteinMPNN is a powerful model for protein sequence design but was trained mainly on large, linear proteins. Consequently, it does not capture the sequence–structure relationships of small cyclic peptides, which rely on tight backbone geometry and internal hydrogen-bonding networks.
🎯 CyclicMPNN addresses this gap by fine-tuning ProteinMPNN on cyclic peptide sequence–backbone pairs validated for structural compatibility using HighFold, enabling more accurate sequence design for cyclic backbones.
🔬 Key Applications & Insights
1️⃣ Reliable Sequence Design for De Novo Cyclic Backbones
CyclicMPNN assigns sequences to GenKIC, RFPeptide, or CyclicCAE backbones in a single step, learning the rules required to satisfy tight cyclic geometry without repeated refinement.
2️⃣ Motif-Inpainting for Therapeutic Design
CyclicMPNN preserves the Nrf2 EETG motif while stabilizing the surrounding cycle, maintaining motif geometry while enabling scaffold design. This capability is critical for designing cyclic peptides that retain functional binding sites.
3️⃣ Accurate Structural Recapitulation Without Iteration
CyclicMPNN achieves ≤ 1 Å RMSD to target backbones without Rosetta relax or redesign cycles by learning true backbone compatibility. This eliminates the need for computationally expensive iterative refinement.
4️⃣ Energetically Stable Folding Funnels
Sequences designed by CyclicMPNN show strong PNear funnels, indicating genuine thermodynamic stability rather than only structural agreement. This ensures designs will fold reliably in experimental conditions.
💡 Why It’s Cool
CyclicMPNN overcomes a key bottleneck in cyclic peptide design by enabling reliable sequence assignment for constrained backbones. By learning the sequence rules unique to cyclic systems, it improves structural accuracy, stability, and motif preservation without iterative refinement.
This approach streamlines cyclic peptide design workflows and provides a framework for adapting protein design models to other constrained biomolecular systems.
📃 Read the paper
⚙️ Try the code
Big thanks to Amber Vig for writing this article, another great find!
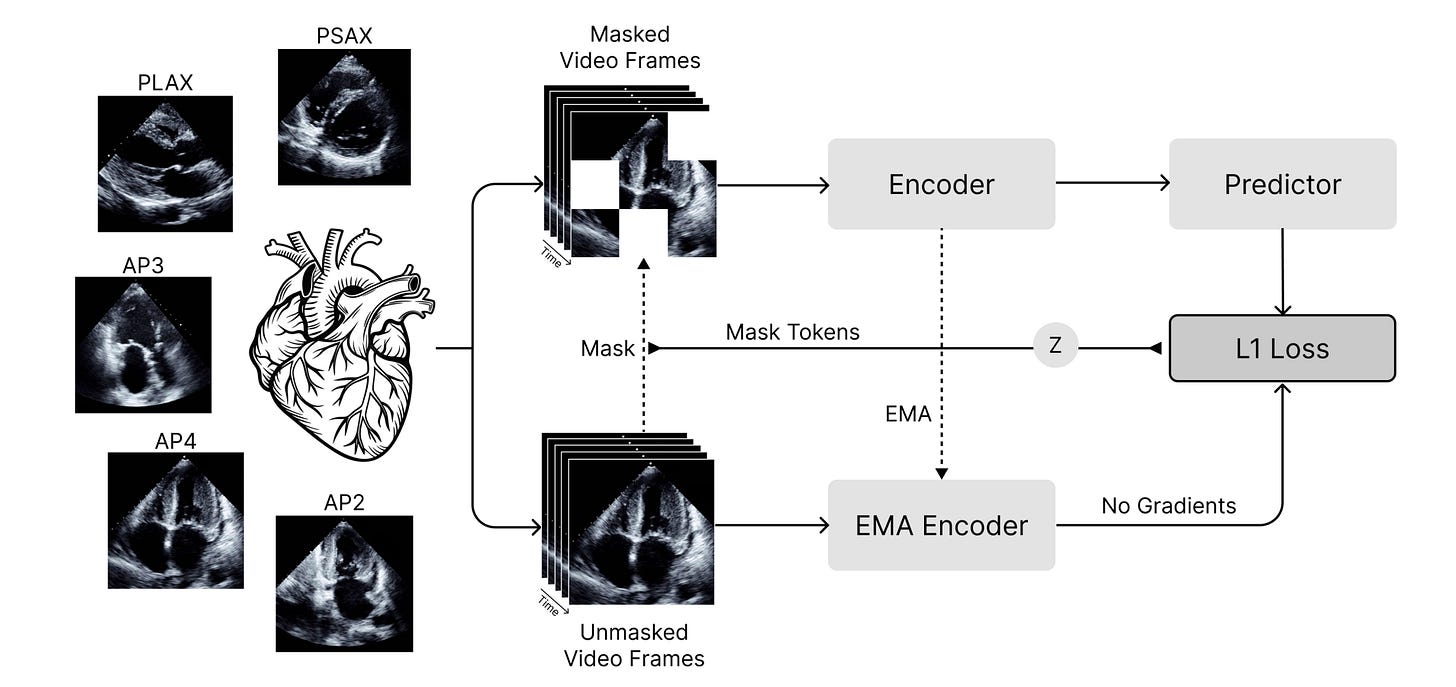
🫀 EchoJEPA: Learning Cardiac Anatomy Without Memorising Speckle Noise
That’s the challenge EchoJEPA tackles, a foundation model from University Health Network, University of Toronto, and collaborators trained on 18 million echocardiograms. Instead of reconstructing pixels (and their noise), it predicts latent representations, learning what’s anatomically stable whilst ignoring acoustic artifacts.
Ultrasound is tricky. Speckle, depth attenuation, and acoustic shadows dominate images but tell you nothing about cardiac anatomy. EchoJEPA uses joint-embedding predictive architectures (JEPA) to downweight unpredictable noise and reinforce temporally coherent structures like chamber walls and valve motion.
🩺 Applications and Insights
1️⃣ Latent beats pixel reconstruction
In a compute-matched comparison, EchoJEPA-L outperformed VideoMAE by 27% on LVEF estimation and 45% on view classification — identical architecture and data, only the objective differed.
2️⃣ Remarkable sample efficiency
Achieved 79% view classification accuracy with just 1% of labelled data, versus 42% for the best baseline trained on 100%. A game-changer for medical AI where annotations are expensive.
3️⃣ Superior robustness
Under physics-informed perturbations (depth attenuation, acoustic shadows), EchoJEPA degraded by only 2% compared to 17% for competitors — 86% less sensitivity to artifacts that plague clinical imaging.
4️⃣ Zero-shot paediatric transfer
Trained entirely on adult data, zero-shot performance on paediatric patients (4.32 MAE) beat all baselines after fine-tuning, proving the representations genuinely capture cardiac anatomy.
💡 Why It’s Cool
EchoJEPA shows that matching your learning objective to domain physics matters enormously. By focusing on what’s predictable (anatomy) versus what isn’t (speckle), it builds representations that generalise across acquisition conditions, patient populations, and age groups. The sample efficiency with frozen backbones lowers barriers for clinical researchers lacking compute budgets for end-to-end fine-tuning.
📖 Read the paper.
💻 Try the code
Thanks for reading!
💬 Get involved
We’re always looking to grow our community. If you’d like to get involved, contribute ideas or share something you’re building, fill out this form or reach out to me directly.
Connect With Us
Have questions or suggestions? We'd love to hear from you!
📧 Email Us | 📲 Follow on LinkedIn | 🌐 Visit Our Website